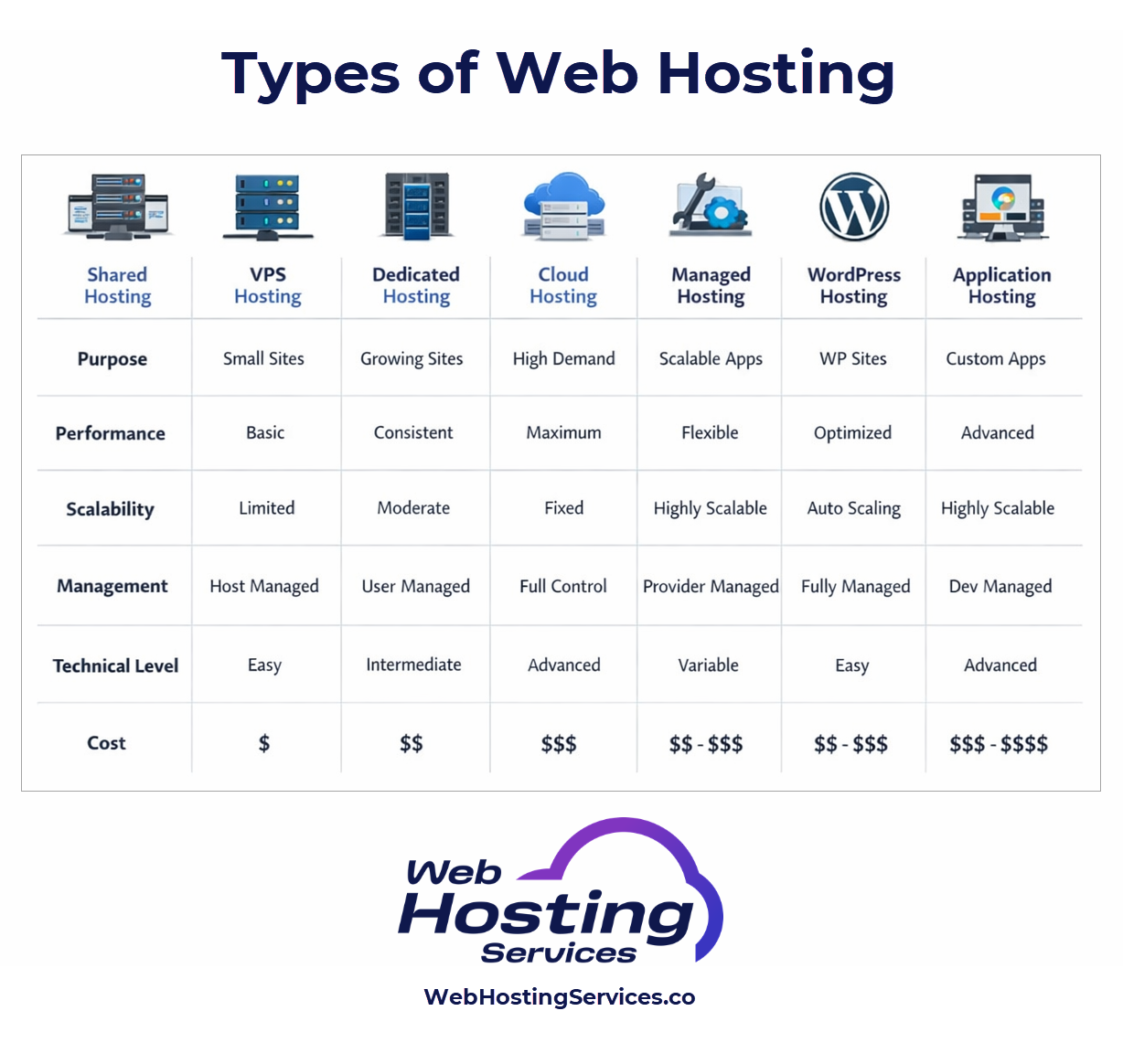
Key Takeaways
- Shared hosting is the simplest option for beginners with small websites
- VPS hosting provides isolated resources and more control for growing projects
- Dedicated hosting offers full hardware control for high performance needs
- Cloud hosting uses distributed infrastructure to scale based on demand
- Managed hosting reduces technical workload for users who prefer simplicity
- WordPress hosting optimizes performance for WordPress based websites
- Application hosting supports complex apps with custom frameworks and backend logic
- Understanding DNS, servers and resource allocation helps beginners choose the right hosting
If you are building your first website, choosing the right type of web hosting can feel like sorting through a maze of technical terms. In practice, each hosting type follows a simple pattern. Every website needs storage, a server that can respond to visitors and a stable network connection. The hosting model you choose defines how much control you have, how many resources you get and how your site scales as it grows.
This guide breaks down the major types of web hosting in a beginner friendly way. You will learn how shared hosting, VPS hosting, dedicated servers and cloud hosting work. You will also see how managed hosting, WordPress hosting and specialized platforms fit into the landscape. Along the way, you will see references to trusted documentation from Mozilla MDN, Cloudflare, WordPress.org, AWS, Microsoft Learn and ICANN so you can explore the underlying technology with confidence.

What Web Hosting Really Means
Before exploring the categories of hosting, you need a clear picture of what hosting actually does. Hosting stores your website’s files on a server that stays online so visitors can access your content. Every time someone types your domain name, their browser sends a request through DNS, reaches your server’s IP address and loads your pages. Documentation from Mozilla MDN explains this request and response cycle in detail.
Your hosting provider supplies key pieces of infrastructure. This includes server hardware, storage, an operating system, network connectivity and security layers. You manage your site through a control panel or dashboard where you upload files, install applications and configure DNS. Hosting is the digital home where your website lives, and different hosting types provide different levels of space, stability and control.
Understanding this foundation helps you choose hosting based on actual needs instead of guesswork. The rest of this guide explains each hosting type in depth so you can decide which environment fits your goals.

Shared Hosting Explained
Shared hosting is the most beginner friendly option. Your website lives on a server with many other websites. You share CPU, memory and storage with other accounts, which keeps the cost low. Shared hosting providers often include helpful tools such as one click installers, file managers and website builders.
Shared hosting works best for small sites with predictable traffic. Personal blogs, small business pages or simple portfolios can run smoothly in this environment. With shared hosting, you rarely need to manage server configuration. The host handles updates, resource management and security at the server level. This makes the experience easier for beginners who only need a place to launch a website.
Most shared hosts also provide integrated DNS tools, basic email hosting and automated SSL certificates. Providers use optimized server stacks running applications like Apache or Nginx behind the scenes. You can explore how these web servers work at Mozilla MDN to understand what serves your files.
Shared hosting is not suited for high traffic sites or heavy applications, but it offers a simple starting point for learning how websites work.

VPS Hosting Explained
A Virtual Private Server, or VPS, gives you a slice of a server with dedicated resources. Instead of sharing CPU and memory in an open pool, virtualization technology creates isolated environments. You get your own operating system, private storage and consistent performance. Providers use hypervisors to divide hardware into virtual machines. This is similar to how cloud providers segment resources across instances.
VPS hosting fits websites that have outgrown shared plans. For example, a blog with thousands of visits per day, an online store with real time transactions or an application that requires specific server configuration. With a VPS, you gain more control over software installations and performance tuning.
You can manage your VPS through SSH or a control panel depending on the host. You can install packages, configure firewalls, optimize databases or customize server settings. Guides from Microsoft Learn and AWS can help you explore operating system and server administration concepts.
While a VPS offers flexibility, you also take on more responsibility. You are expected to update software, manage security rules and monitor resource usage. For users comfortable with light server management, VPS hosting offers a strong balance of power and affordability.

Dedicated Hosting Explained
Dedicated hosting gives you full access to an entire physical server. No other customers share your hardware or resources. This is the most powerful hosting model outside of cloud architecture and is ideal for demanding projects that require high performance, isolation or custom infrastructure.
A dedicated server lets you choose the operating system, configure security rules, install frameworks and optimize performance for your specific application. Large e commerce stores, enterprise platforms and data intensive projects often rely on dedicated servers for stability.
Because you control everything, you also handle more administrative work. You are responsible for updates, security hardening, user access controls and monitoring. Hosting providers offer managed dedicated plans for users who want the hardware benefits without the workload.
You can explore server administration concepts in detail through Microsoft Learn or Linux documentation. Dedicated hosting is often the next step once VPS or cloud environments need even greater consistency and isolation.

Cloud Hosting Explained
Cloud hosting uses distributed infrastructure to host your site across multiple servers rather than a single machine. Your website runs on virtual instances that can scale up or down based on demand. Cloud platforms such as AWS, Google Cloud and Microsoft Azure rely on large data center networks to provide flexible capacity, global reach and reliable uptime.
AWS describes cloud compute models and virtualization principles in its compute overview. Understanding these resources helps beginners grasp why cloud hosting feels more dynamic than traditional hosting.
Cloud hosting suits websites with variable traffic, modern applications, APIs or services that require predictable scaling. You can deploy instances in specific regions, replicate content across zones and add or remove compute power when needed.
With cloud environments, you often use dashboards, command line tools or automation scripts to manage deployments. You can integrate load balancers, managed databases, file storage services and CDNs for performance. Cloud hosting offers strong reliability because your site does not rely on a single physical server.

Managed Hosting Explained
Managed hosting takes the technical tasks off your plate. Instead of managing updates, security patches and performance settings yourself, the hosting provider handles them. Managed hosting is available for VPS, dedicated and cloud setups.
This type of hosting is ideal if you want strong infrastructure without day to day server management. Managed hosting providers monitor performance, update software, configure backups and secure the server. They often include managed migrations and support for troubleshooting issues.
Managed hosting is especially common for WordPress. Many providers offer optimized WordPress environments with caching layers, automatic updates and staging sites. WordPress explains installation and hosting principles on WordPress.org. With managed hosting, you can focus on content and features instead of infrastructure.
This model is helpful for small teams, beginners or anyone who prefers a hands off approach to technical operations.

WordPress Hosting Explained
WordPress hosting is a specialized hosting environment created for WordPress websites. The servers are configured for PHP, MySQL or MariaDB and optimized for caching and performance. Many hosts include tools for automatic WordPress updates, plugin management and security hardening.
This type of hosting removes guesswork from the setup. You can use one click installers or pre configured environments. Performance layers often include server level caching and optimized database settings. WordPress hosting is not required to run WordPress, but it can make life easier.
Users who want simple management and fast WordPress performance benefit most from this model. You can explore WordPress requirements at WordPress.org to understand why specialized hosting can help.

Cloud Platforms and Application Hosting
Some websites are actually applications with backend processes, APIs and complex workflows. Cloud platforms host these applications using compute instances, containers or serverless functions. AWS offers services such as EC2, ECS and Lambda, which you can explore in the AWS documentation. Microsoft Azure provides parallel options documented through Microsoft Learn.
These platforms let you deploy apps in ways that traditional shared hosting cannot. You can scale backend processes, integrate managed databases, connect load balancers and use advanced networking. Application hosting is more technical but offers the most freedom for developers building custom services.
Beginners who plan to grow into building more advanced applications often use cloud platforms once they understand the basics of hosting.

Comparing Hosting Types Side by Side
Choosing the right hosting type is easier when you compare your needs with what each model provides. Here is a clear way to think about it without relying on jargon.
- Shared hosting is inexpensive and easy but offers limited resources.
- VPS hosting provides consistent performance and greater control.
- Dedicated hosting delivers maximum isolation and power.
- Cloud hosting scales dynamically and supports global performance.
- Managed hosting reduces workload across all hosting levels.
- WordPress hosting is tailored specifically for WordPress sites.
- Application hosting supports complex custom applications.
Your choice depends on your traffic expectations, technical skill and long term project goals. By grounding your decision in real operational needs, you avoid both overspending and choosing a platform that cannot support your site’s growth.
References & Additional Resources
- Mozilla MDN HTTP Overview
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Overview - Cloudflare DNS Documentation
https://developers.cloudflare.com/dns/ - WordPress.org, How to Install WordPress
https://wordpress.org/support/article/how-to-install-wordpress/ - AWS Compute and Networking Overview
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/whitepapers/latest/aws-overview/compute-and-networking-services.html - Microsoft Learn, Windows Server Documentation
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/ - ICANN Domain System Resources
https://www.icann.org/resources/pages/welcome-2012-02-25-en
Tagged In:
- Beginner Hosting, Choosing Hosting, Cloud Hosting, Cloud Servers, Dedicated Hosting, DNS, Domain Name System, Domain Names, Hosting Infrastructure, Hosting Overview, Hosting Plans, Hosting Servers, Managed Hosting, Physical Servers, Shared Hosting, Virtual Servers, VPS Hosting, Web Hosting Basics, Website Beginners
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this article is for general educational and informational purposes only. While we strive to keep content accurate and current, web hosting technologies, pricing, features, discounts, and best practices can change over time and may vary by provider.
This content is not intended to constitute professional, legal, financial, or technical advice. Readers should independently verify pricing, features, and terms directly with hosting providers and consult qualified professionals when making decisions related to web hosting services, infrastructure, or website deployment.
References to third-party tools, platforms, services, pricing, or promotions are provided for informational purposes only and do not constitute endorsements. We make no guarantees regarding pricing accuracy, availability, performance, security, discounts, or outcomes based on the use of any hosting service discussed.
I am a web hosting specialist with over 15 years of experience in digital marketing, web design, and website and hosting management. My background includes managing and maintaining websites for clients across a wide range of industries, with a long-standing focus on building and supporting search engine optimization friendly websites.
My work sits at the intersection of hosting infrastructure, website performance, and real-world usability. Over the years, I’ve worked extensively with hosting environments, domain systems, DNS configuration, and server platforms while also designing and managing websites that need to perform reliably in search results, under traffic, and over time.
This site exists to explain web hosting clearly and accurately, based on hands-on experience rather than marketing claims.
- This author does not have any more posts.